Understanding the Basics of Public Key Cryptography

With the increasing risk of cybercrime and data theft, many organizations and individuals are practicing cybersecurity measures to protect their sensitive information. Public key cryptography is one of the most popular encryption methods used in cybersecurity. But what does it mean? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the basics of public key cryptography and how it differs from traditional cryptography.

What is Public Key Cryptography?
Public key cryptography is an encryption method that uses two keys, i.e., a public key and a private key. The public key is accessible to everyone, whereas the private key is only accessible to the owner. This method is also called asymmetric cryptography because the encryption and decryption keys are two separate entities. Data encrypted with a public key can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key.
Additionally, this type of cryptography is used for digital signatures and authentication. A message encrypted with a sender’s private key can only be decrypted with the public key of the specified receiver. This ensures the message comes from an authenticated source and has not been tampered with in transit.
Finally, public key cryptography is used for various protocols such as Diffie-Hellman, RSA, and DSA. These protocols offer message confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. If one of these protocols is used, the sender and receiver can securely communicate without any risk of data theft.
How Does Public Key Cryptography Work?

Two keys are used in public key cryptography: a private key, which is known only to the owner, and a public key, which is available to anyone. When data is encrypted with one of these keys, it can only be decrypted with the other.
This means that if someone encrypts data with their private key, anyone who knows the corresponding public key can decrypt it. Similarly, if someone encrypts data with a public key, only the private key owner can decrypt it.
For example, let’s say Alice wants to send Bob a secure. She encrypts it with her private key and then sends it to him. When Bob receives the message, he can decrypt it using Alice’s public key. This ensures the message comes from Alice and has not been tampered with in transit.
Benefits of Public Key Cryptography
Public key cryptography has several advantages over traditional encryption methods:
- It provides authentication, ensuring the message comes from an authorized source and hasn’t been tampered with in transit.
- It doesn’t require sharing a secret key between the sender and recipient.
- It provides secure digital signatures and allows secure communication between two or more parties.
- It offers greater security since it relies on two separate keys instead of just one.
- It allows for secure communication between two parties who may not know each other, which is invaluable in many cyber applications.
- It is also faster and more efficient than other encryption methods.
Differences between Public Key Cryptography and Traditional Cryptography
Public key cryptography is asymmetric cryptography used for secure data communication, whereas traditional cryptography uses a single key for encryption and decryption. As the traditional cryptography method is the same for everyone, the data can be decrypted if a third party intercepts the key. Public key cryptography avoids this situation, as the private key is only accessible to the owner.
For instance, if someone wanted to send a confidential message to another person via email, they could encrypt it with their public key, and the recipient would be able to decrypt it using their private key. This way, only the message’s intended recipient can access its contents.
How Digital Signatures Work?
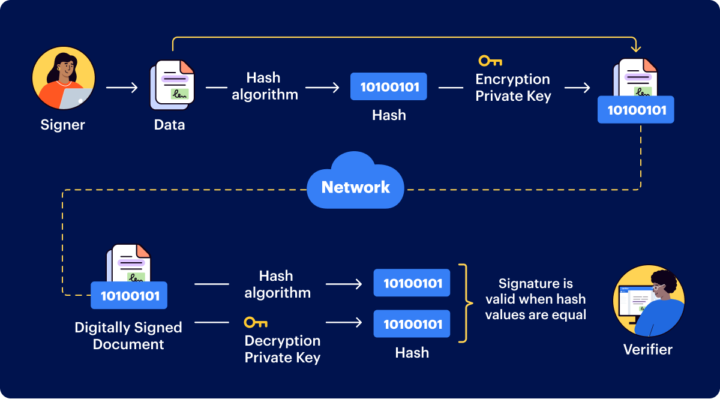
When using digital signatures, both parties involved must have their own pair of keys; one public and one private. The sender first creates a hash (a unique string of numbers) from the original data which will act as an identifier for that particular piece of information. They then encrypt this hash using their private key, creating what is known as a “digital signature” which they attach to the original data before sending it off to its recipient.
Once received, the recipient uses the sender’s public key to decrypt this signature and compare it against their own copy of the original data’s hash – if they match, then they know that no changes have been made during transmission and thus trust in the authenticity of the sender.
In summary, public key cryptography is an important cryptographic technique that provides secure data communication and digital signatures. It utilizes two separate keys instead of one, making it more secure than traditional methods and allowing for secure communication between two parties who may not know each other while also providing authentication to ensure that no tampering has occurred in transit. Digital signatures allow for secure digital documents to be verified and trusted, making public key cryptography an invaluable tool in the modern cyber world.
What If the Keys are Compromised?
Public key cryptography is secure only if the keys remain safe and private. If either key is compromised, the data can be stolen or tampered with. Therefore, it’s important to use strong security measures to protect your keys and data. This includes regularly changing passwords, using two-factor authentication, and using encryption whenever possible. It’s also important to remember to store your keys in a safe place – offline, or locked with a password if kept online – and never share them with anyone else. By following these steps, you can ensure that your data remains secure and protected even if the keys are compromised.
Conclusion

Public key cryptography is a powerful cryptographic tool that provides secure data communication and digital signatures. It allows for safe transmission of confidential information between two parties who may not know each other, as well as authentication to ensure that the message has not been tampered with in transit. However, it’s important to make sure your keys remain secure and private, as compromising them can lead to data theft or tampering. By following the proper security measures and storing your keys in a safe place, you can ensure that your data remains secure even if the keys are compromised.
